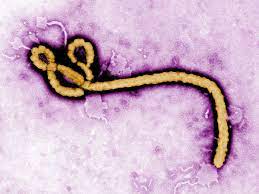
Ebola virus disease (EVD; also Ebola hemorrhagic fever or EHF), or simply Ebola, is a disease of humans and other primates caused by Ebola viruses. Signs and symptoms typically start between two days and three weeks after contracting the virus with a fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches.
Then, vomiting, diarrhoea and rash usually follow, along with decreased functioning of the liver and kidneys. At this time some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease has a high risk of death, killing between 25 and 90 per cent of those infected with an average of about 50 per cent.
This is often due to low blood pressure from fluid loss and typically follows six to sixteen days after symptoms appear. The virus spreads by direct contact with body fluids, such as blood of an infected human being or other animals. This may also occur through contact with an item recently contaminated with bodily....