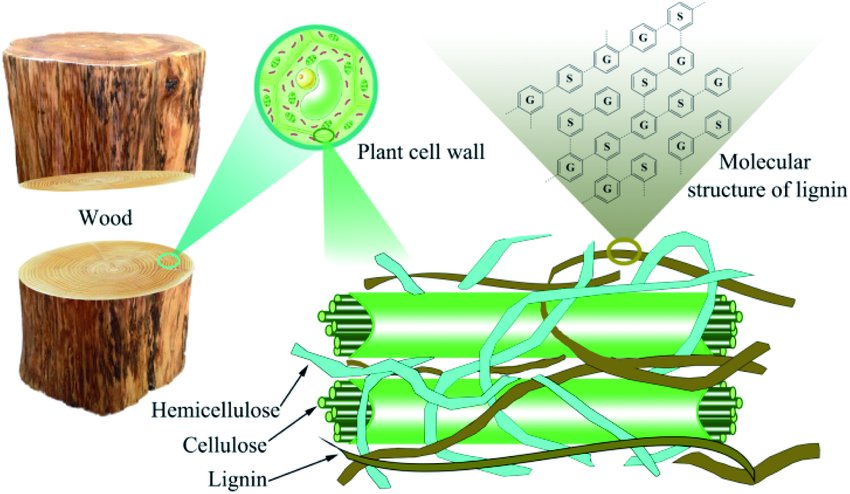
Lignin is a complex oxygen-containing organic polymer that, along with cellulose, forms the main constituent of wood. It is a secondary metabolite concentrated in the cell walls of wood and makes up 24–35 per cent of the oven-dry weight of softwoods and 17–25 per cent of hardwoods.
It is second to cellulose as the most abundant organic material on Earth. The lignin provides compressive strength and stiffness to the plant cell wall and is believed to have played a role in the evolution of terrestrial plants by helping them withstand the compressive forces of gravity.
Lignin also waterproofs the cell wall, facilitating the upward transport of water in xylem tissues. Finally, lignin has antifungal properties and deposited in response to injury by fungi, protecting the plant body from the diffusion of fungal enzymes and toxins.
Chemically, lignin is a phenolic compound and is a mixture of....